Restorative Practices
A growing number of school communities across the United States have begun to explore the use of restorative justice processes as a means of addressing the limitations of these punitive discipline measures. In states like California, Colorado, Maryland, Michigan and Minnesota, educators are implementing a variety of restorative discipline alternatives to traditional measures such as detention, suspension, expulsion, and police charges. In Canada, Ontario educators have created a Restorative Practice Consortium that collects and shares educational resources for restorative work.
Many school districts have found restorative justice to be a more effective means of addressing school and victim safety, and transforming discipline into a learning opportunity. In schools using restorative justice practices, an offending student is given the opportunity to participate in a restorative discipline process as a means of repairing the harm done to those affected by the wrongdoing. These processes are voluntary for the parties and may be offered in lieu of punitive discipline measures, as a re-entry process following traditional discipline, or in combination with reduced sanctions.
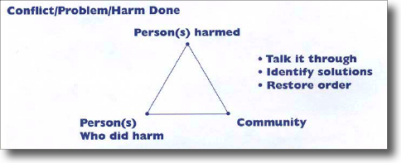
Rather than focusing exclusively on the punishment of offenders and their removal from society, the chief concern of restorative justice is to identify and repair the harm done by crime and wrongdoing to the greatest extent possible. This is achieved by holding offenders directly accountable to those they have harmed, through giving victims a direct voice in the process of repair, restoring the safety and trust within communities, and providing more meaningful outcomes for everyone affected.
Howard Zehr, an early pioneer of this movement, coined three “restorative questions” that have guided these restorative practices around the world. The questions are contrasted below with the “retributive questions” that have characterized the dominant response to crime in Western culture:
Restorative Justice
1. What is the harm that was done?
2. How can that harm be repaired?
3. Who is responsible for this repair?
Retributive Justice
1. What is the law that was broken?
2. Who broke that law?
3. How should they be punished?
Many of the different methods of restorative justice described above, such as victim-offender mediation, community group conferencing, and peacemaking circles, have been found to be useful in school settings. The San Francisco Unified School District’s Restorative Practices Project and University of Maryland CDRUM program offer lots of helpful resources for educators interested in developing a program. A video from the Teacher’s Democracy Project of Baltimore looks at strategies from schools across the country for bringing Restorative Practices to schools. The website Fix School Discipline provides a useful toolkit for educators interested in implementing RJ in their schools.
Videos of Possible Interest
- RJOY – Introducing Restorative Justice for Oakland Youth
- Restorative Justice: It’s Elementary
- Kids rap – conflict resolution and respect
- It’s Time for California Schools to Stop Suspending More Students Than They Graduate
- Conflict Resolution in Public Schools
- Justice Committee: Using Restorative Practices to Resolve Conflicts
- Restorative Justice Takes on Oakland Schools
- Teaching Humanitarian Law with Raid Cross
- In a Responsive Classroom
- Restorative Practices and Texting While Driving
- Restorative Justice at Mountain View Alternative HS
- An Alternative to In-School Suspension
- Restoring Schools
- Restorative Justice Arts Initiative
- TEDx Talk: Restorative Practices to Resolve Conflict and Build Relationships
- The Forum: Conflict Resolution in a Circle
- Quality Education to Build Peace
- The Transformation of West Philadelphia High School: a story of hope
- Schools resolve conflicts by getting kids to talk things out (PBS NewsHour)
See MORE VIDEOS...
Sample Catalog Resources
Below you'll find a randomized listing of up to 20 related items (we may have more...) drawn from our Resource Catalog.
| Resource Title | Description | Links |
|---|---|---|
| Program theory for restorative practices in schools | Handout which charts how restorative practices function in schools. | |
| How We Can Fix School Discipline Toolkit | The 77-page 'How We Can Fix School Discipline Toolkit' contains step-by-step tools and real-life stories about implementing the alternatives to suspension and expulsion that are proven to keep students in school and learning, improve school climate and student behavior, allow teachers to teach more effectively, help administrators meet benchmarks, and keep communities from seeing many of their children ending up in the juvenile justice system. Alternative approaches featured include School-Wide Positive Behavioral Intervention and Support (SWPBIS), Restorative Justice or Restorative Practices, and Social Emotional Learning. The document is structured as follows: 1. Know the problem (pages 4-10) 2. Learn about alternatives from real-life examples (pages 11-48) 3. Advocate for Change (page 63) 4. Monitor progress (pages 68-70) 5. Get the word out (pages 64-67) 6. Contacts (pages 71-78) A companion website is available at http://www.fixschooldiscipline.org. A video archive of a webinar introducing the toolkit is available at http://youtu.be/6PrCh0MiRZc | |
| Restorative justice for the classroom: Lesson 1 the community web | 3-page pdf lesson "to identify community roles in conflict resolution and develop understanding of the significance of each role in keeping the community safe. Through role play, students learn how each role is a part of an intricate web of community support and how a breakdown in one part of the web affects the whole. Through this lesson students develop communication skills and empathy." | |
| Making things right: Restorative justice comes to campuses | Pdf article from Conflict Management in Higher Education Report, Volume 1, Number 1, (Jan/Feb 2000), discussing the use of restorative justice principles for "creative options to traditional justice systems, options which are flexible enough to allow positive productive responses to a variety of offenses or violations and which also meet the unique needs of the University community." | |
| Continuum of [restorative justice] strategies | 1-page PDF chart illustrating a continuum of restorative justice strategies, with an informal end where staff are provided with skills of how to engage young people in a dialogue that emphasises a greater sense of other and a more formal end with skills to restore damaged relationships following an incident or outburst. | |
| Facilitation Guide for Restorative Justice Community Accountability Panel Members | This manual is designed to assist a Trainer in conducting sessions for the purpose of teaching facilitation skills to members of Restorative Justice Community Accountability Panels, or other models of Restorative Justice. It was prepared by using taped transcripts of Training Sessions held for Chilliwack Restorative Justice and Youth Diversion Association, presented by Wendy Burton, professor at the University College of the Fraser Valley. Content has been edited. The information contained in this manual covers the basics of communication and facilitation skills. The manual contains three parts: a participant guide, a trainer's guide, and a collection of handouts and exercises. | |
| The Challenge of Culture Change: Embedding Restorative Practice in Schools | Paper presented at the Sixth International Conference on Conferencing, Circles and other Restorative Practices: “Building a Global Alliance for Restorative Practices and Family Empowermentâ€. Sydney, Australia,March 3-5, 2005. Argues that Restorative practice, with its emphasis on relationships, demands that schools attend to all aspects of the school culture and organisation and that they develop a range of relational practices that help prevent incidents of inappropriate behaviour from arising in the first place. Presents stages for the implementation of this kind of cultural change process. | |
| RESTORE Our Schools | This 10-page document entitled RESTORE provides a restorative perspective that can inform how we plan for the return to the classrooms, playgrounds and corridors of physical schools. It highlights seven key areas which, alongside learning, are where we need to stimulate thinking and make decisions in order to collectively move forward into a healthy ‘new normal’. The areas intersect, interconnect and affect each other, as we all do. RESTORE is a lens through which staff, children and parents can look at the strategy and plans that are needed for everyone’s well-being in a fast changing environment and for a safe and healthy return to school. The seven themes represented by the seven letters of the word RESTORE emerged from discussions on the current pandemic and its impact on us all, but particularly on schools: the students, parents and care-givers and the school staff. The letters of the word RESTORE, could be seen as falling into two areas of need, one the recent past and our experiences of it, and the other looking ahead to how we want to be as a result of this experience: The first four letters of the acronym, relating to Recognise, Empathise, Safety and Trauma, are connected to what has happened and its effects on us. The last three letters, relating to Opportunity, Relationships and Engagement, are key to how we are going forward into a new normal. | |
| Restorative justice programs in schools | Web-site created by the Marist Youth Care organization with information about restorative justice programs. "Marist Youth Care is a not for profit agency dealing with at risk young people. We draw our energy and motivation from the call of the gospel to assist socially disadvantaged people to take their rightful place in the community," from the Marist Youth Care website. | |
| RESTORE: Activities to support secondary pupils during COVID-19 | ||
| Restorative Practices in Catholic School Communities: Audit Tools | 33-page pdf providing 9 different assessment instruments for schools developing restorative practice initiatives. Prepared in Australia, "The...Audit Tools for Restorative Practices have been developed by the Student Wellbeing Team of the Catholic Education Office (Melbourne) for use by the Core Leadership Team and staff in the school. The purpose of the tools is to provide...both quantitative and qualitative data regarding the implementation of Restorative Practices strategies at the school level." | |
| A Social Justice Lens: A Teaching Resource Guide | This 12-page guide provides a lens that applies social justice and critical theory to all aspects of an educators professional life. The tool provides a framework for unions and schools to help guide policy, plan actions, and evaluate resources for social change. Social justice theory focuses on equity for all and critical theory requires action and systemic change. These two concepts form the basis of the British Columbia Teachers Federation social justice lens. The lens has four distinct interconnecting filters -- access, agency, advocacy, and solidarity action. Each represents an aspect of social justice work, and, while we may focus on one filter at a time, the true potential of these filters lies in engaging with all four simultaneously. Participatory democracy, civil society, transformative practice, and systemic change found on the rotating outer ring of the lens are necessary to achieve the ultimate goal of equity found at the centre of the lens. | |
| A Generation Later: What We've Learned about Zero Tolerance in Schools | Zero tolerance discipline policies that mandate suspension or expulsion of students for misconduct have gained tremendous momentum over the past 25 years while also inviting deep controversy. With A Generation Later: What We’ve Learned about Zero Tolerance in Schools, Vera’s Center on Youth Justice looks at existing research about whether zero tolerance discipline policies make schools more orderly or safe, if out-of-school suspension or expulsion leads to greater involvement in the juvenile justice and criminal justice systems, and what effect these policies can have on a young person’s future. It concludes that, a generation after the rise of these policies and practices, neither schools nor young people have benefited. Fortunately, as described in the report, promising alternatives to zero tolerance can safely keep young people where they belong -- in school. | |
| National evaluation of the restorative justice in schools programme | 99-page pdf document which provides the findings of national (England and Wales), "projects [which] spanned a range of different approaches to introducing restorative practices into schools, including restorative justice conferences ... the contract to evaluate these initiatives was awarded to Partners in Evaluation, a specialist agency with a multi-ethnic team of researchers and a national reputation for conducting evaluations in the fields of health, education, social exclusion and regeneration." Includes a literature review, sample pupil and school staff surveys and post-conference interview schedule for perpetrators and aggrieved. | |
| Restorative Interventions Implementation Tool Kit | Implementation tools and resources for school staff and other adults trained to facilitate conferences and circles to repair harm in educational settings. The tools and resources are designed to assess readiness, implementation and outcomes, as well provide guidance for implementing any school-based restorative model. | |
| Restorative justice in the classroom: Lesson 5 the justice circle part 3 | 8-page pdf lesson which provides "students with an opportunity to learn and practice the facilitation of Justice Circles. After a review of the purpose and process, students role-play scenarios, covering all roles including the role of facilitator. After their role-play experience, students discuss whether the circle would be effective in both healing the victim and helping the offender learn a better way to behave, and explore what could have been done differently to more effectively meet those objectives." | |
| Restorative conferences resource kit | 60-page pdf resource kit for presenting restorative conferences which "(involves the gathering of those who have a stake in a particular troublesome situation, to talk together to find ways of making amends) ... the purpose of these conferences is to discuss what the problem might be and to pool ideas about what might be most helpful from here, for all concerned, from this pool of ideas should emerge a plan for restoration of the situation... These Conferences offer a helpful step forward by involving a range of participants who both contribute to and are affected by the situation at hand, they promote a spirit of open and direct conversation and add a human touch to the process of addressing transgressions... this Resource Kit represents the culmination of 18 months of work by a group whose links are with restorative justice, Maori protocols, and counsellor training with narrative therapy at the University of Waikato." Includes bibliography | |
| Implementing restorative justice: A guide for schools | This 24-page pdf is designed to introduce the concepts of restorative justice and restorative discipline to school personnel. "The guide advises on the use of the restorative justice philosophy to achieve student accountability, competency development, as well as community safety. The guide is specifically designed to provide Illinois school personnel and families with practical strategies to use restorative justice in their daily activities." | |
| Restorative Approaches in Schools A Guide for School Managers and Governors | Restorative approaches provide schools with a range of practices which promote mutually respectful relationships and manage behaviour and conflict, address bullying and absences and build community cohesion. Restorative approaches are not new, but offer a framework upon which to build on existing good practice. There is a wealth of evidence that shows how the use of restorative approaches alongside Social and Emotional Aspects of Learning (SEAL), helps to develop more resilient and self regulating learners, thus creating positive learning environments. This 25-page guide describes the underpinning philosophy of restorative approaches and their links to current developments in education, gives advice on implementation and through case studies, shows the impact on individuals, classes and whole school policy and practice. It sets out how restorative approaches can create a positive ethos, change perspectives of pupils, staff and parents and offer viable and successful alternatives to traditional conflict resolution approaches. The purpose is to connect and re-engage everyone on the learning journey. | |
| Kids Working It Out Resource Appendix | A listing of books, publications and websites provided in the appendix to Tricia S. Jones and Randy O. Compton (Eds.) 2003 book Kids Working It Out: Stories and Strategies for Making Peace in Our Schools. |
