Restorative Practices
A growing number of school communities across the United States have begun to explore the use of restorative justice processes as a means of addressing the limitations of these punitive discipline measures. In states like California, Colorado, Maryland, Michigan and Minnesota, educators are implementing a variety of restorative discipline alternatives to traditional measures such as detention, suspension, expulsion, and police charges. In Canada, Ontario educators have created a Restorative Practice Consortium that collects and shares educational resources for restorative work.
Many school districts have found restorative justice to be a more effective means of addressing school and victim safety, and transforming discipline into a learning opportunity. In schools using restorative justice practices, an offending student is given the opportunity to participate in a restorative discipline process as a means of repairing the harm done to those affected by the wrongdoing. These processes are voluntary for the parties and may be offered in lieu of punitive discipline measures, as a re-entry process following traditional discipline, or in combination with reduced sanctions.
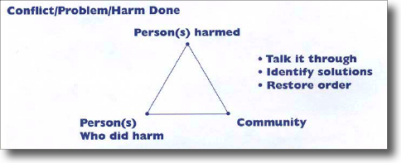
Rather than focusing exclusively on the punishment of offenders and their removal from society, the chief concern of restorative justice is to identify and repair the harm done by crime and wrongdoing to the greatest extent possible. This is achieved by holding offenders directly accountable to those they have harmed, through giving victims a direct voice in the process of repair, restoring the safety and trust within communities, and providing more meaningful outcomes for everyone affected.
Howard Zehr, an early pioneer of this movement, coined three “restorative questions” that have guided these restorative practices around the world. The questions are contrasted below with the “retributive questions” that have characterized the dominant response to crime in Western culture:
Restorative Justice
1. What is the harm that was done?
2. How can that harm be repaired?
3. Who is responsible for this repair?
Retributive Justice
1. What is the law that was broken?
2. Who broke that law?
3. How should they be punished?
Many of the different methods of restorative justice described above, such as victim-offender mediation, community group conferencing, and peacemaking circles, have been found to be useful in school settings. The San Francisco Unified School District’s Restorative Practices Project and University of Maryland CDRUM program offer lots of helpful resources for educators interested in developing a program. A video from the Teacher’s Democracy Project of Baltimore looks at strategies from schools across the country for bringing Restorative Practices to schools. The website Fix School Discipline provides a useful toolkit for educators interested in implementing RJ in their schools.
Videos of Possible Interest
- Schools resolve conflicts by getting kids to talk things out (PBS NewsHour)
- The Transformation of West Philadelphia High School: a story of hope
- In a Responsive Classroom
- Kids rap – conflict resolution and respect
- Teaching Humanitarian Law with Raid Cross
- TEDx Talk: Restorative Practices to Resolve Conflict and Build Relationships
- Restorative Justice Takes on Oakland Schools
- Restoring Schools
- Conflict Resolution in Public Schools
- Quality Education to Build Peace
- Restorative Justice: It’s Elementary
- Restorative Justice Arts Initiative
- The Forum: Conflict Resolution in a Circle
- RJOY – Introducing Restorative Justice for Oakland Youth
- Justice Committee: Using Restorative Practices to Resolve Conflicts
- It’s Time for California Schools to Stop Suspending More Students Than They Graduate
- Restorative Justice at Mountain View Alternative HS
- Restorative Practices and Texting While Driving
- An Alternative to In-School Suspension
See MORE VIDEOS...
Sample Catalog Resources
Below you'll find a randomized listing of up to 20 related items (we may have more...) drawn from our Resource Catalog.
| Resource Title | Description | Links |
|---|---|---|
| What have I done: Victim empathy pack responsibility exercises | 13-page Word document presenting a "new victim empathy resource designed to keep victim awareness high in Restorative Justice practitioner's priorities." Contains a number of exercises about taking responsibility for one's actions and exploring feelings. | |
| Parent-To-Parent Guide on Restorative Justice | This "Parent-to-Parent Guide to Restorative Justice in the Chicago Public Schools" provides background on POWER-PAC’s Elementary Justice Campaign and their work to end “zero-tolerance†policies and bring restorative justice to the schools. It also gives suggestions for parents wanting to bring restorative practices to their schools. | |
| Restorative justice in the school setting: A whole school approach | 12-page PDF paper promoting the teaching of restorative justice in schools. "Restorative justice is a philosophy and a set of practices that embraces the right blend between a high degree of discipline that encompasses clear expectations, limits and consequences and a high degree of support and nurturance." | |
| Statement of restorative justice principles: As applied in a school setting: 2nd edition | 24-page PDF document of "Principles [which] form the basis for restorative practices in all settings, using all models, where the primary aims are to repair harm and promote dialogue ... Restorative practices are underpinned by a set of values, these include: Empowerment, honesty, respect, engagement, voluntarism, healing, restoration, personal accountability, inclusiveness, collaboration, and problem-solving." | |
| National evaluation of the restorative justice in schools programme | 99-page pdf document which provides the findings of national (England and Wales), "projects [which] spanned a range of different approaches to introducing restorative practices into schools, including restorative justice conferences ... the contract to evaluate these initiatives was awarded to Partners in Evaluation, a specialist agency with a multi-ethnic team of researchers and a national reputation for conducting evaluations in the fields of health, education, social exclusion and regeneration." Includes a literature review, sample pupil and school staff surveys and post-conference interview schedule for perpetrators and aggrieved. | |
| Promoting SEAL through circle time | 7-page PDF document promoting Social and Emotional Aspects of Learning through circle time for secondary students. "Circle time sessions provide a potential vehicle for the classroom delivery of the SEAL curriculum. Circle time is a time set aside each week when a whole class of young people and their teacher sit in a circle and explicitly engage in a structured programme of games, experiential activities, discussion and relaxation strategies ... It aims to provide an emotionally safe forum for participants to engage with a range of key issues, including peer relationships, conflict resolution, shared goal setting, justice, friendship, democratic principles, respect for individual differences and freedom of choice." | |
| Continuum of [restorative justice] strategies | 1-page PDF chart illustrating a continuum of restorative justice strategies, with an informal end where staff are provided with skills of how to engage young people in a dialogue that emphasises a greater sense of other and a more formal end with skills to restore damaged relationships following an incident or outburst. | |
| Restorative justice in the classroom: Lesson 5 the justice circle part 3 | 8-page pdf lesson which provides "students with an opportunity to learn and practice the facilitation of Justice Circles. After a review of the purpose and process, students role-play scenarios, covering all roles including the role of facilitator. After their role-play experience, students discuss whether the circle would be effective in both healing the victim and helping the offender learn a better way to behave, and explore what could have been done differently to more effectively meet those objectives." | |
| Facilitating Restorative Group Conferences | Facilitating Restorative Group Conferences is a curriculum (6-sessions in length) designed for training volunteer and employed facilitators who will conduct restorative group conferences. It is provided as a set of files for participants and a set of files, including powerpoints, for trainers. A restorative group conference, as used here, refers to a process that seeks to identify, repair and prevent harm, based in restorative justice values including meaningful accountability. A restorative group conference is led by a trained facilitator and involves face-to-face contact among one or more victims or their representative, the offenders, supporters for both, and other people who are affected. Participation of the victim is completely voluntary, and participation of the offender is based upon their willingness and readiness. Development of this curriculum is a project of the Minnesota Department of Corrections, made possible through financial support from the National Institute of Corrections Technical Assistance program. | |
| Community justice in the campus setting | Pdf article from Conflict Management in Higher Education Report, Volume 3, Number 1, (Oct 2002), which examines the idea of community justice and how it can be used on college campuses to address student misconduct and improve socialization. Includes bibliography. | |
| Addressing off-campus student conduct with restorative justice | Pdf article from Conflict Management in Higher Education Report, Volume 6, Number 1, (Nov 2005), which introduces a program where "over 200 students ... participated in restorative justice, meeting face-to-face with community members, fellow students, and campus staff to resolve their cases at the neighborhood level, the results of their conference agreements include hundreds of hours of service in the neighborhoods affected (picking up litter, tutoring at a gradeschool, volunteering at the local library, serving meals to the homeless, etc.), plus written apologies, verbal apologies to neighborhood boards, outreach and education efforts on campus, and in some cases, self-help such as chemical dependency counseling." | |
| Restorative Practices: Fostering Healthy Relationships and Promoting Positive Discipline in Schools | As educators partner with districts to move away from zero tolerance discipline policies and ramp up e orts to strengthen safe and supportive schools, address con ict, improve school climate, and build a positive school culture that students are connected to, many campuses are looking to implement alternative, restorative approaches. This toolkit was developed to illustrate how restorative strategies can be seamlessly integrated into the classroom, curriculum, and culture of schools. It de nes what restorative practices are, explains why they are a transformational tool for fostering healthy relationships in schools and shows how they can be useful processes for students, educators, and learning communities. This toolkit is intended for all educators who support the growth and health of students in schools. It is an introduction for those new to the concepts and will help support and enhance the work of teachers already implementing these practices in their classrooms. e toolkit includes digestible models, frameworks, and action steps for school-wide implementation, accompanied by guiding questions to support re ection for practitioners looking to make restorative methods part of the fabric of daily life in schools. It also recognizes the signi cant role all education professionals play in maintaining a school community that models respectful, trusting, and caring relationships. | |
| Restorative Justice: A Working Guide for Our Schools | The purpose of this publication, available as a 43-page pdf, is to provide support and guidance for teachers, health workers, community leaders, and school personnel who seek to implement Restorative Justice in their schools. The guide introduces Restorative Justice concepts, articulates what is new about the approach, explores benefits, outcomes and impacts and provides guidance on initiating Restorative Justice at the school or district level. Also included are listings of resources for additional information and support. | |
| Making things right: Restorative justice comes to campuses | Pdf article from Conflict Management in Higher Education Report, Volume 1, Number 1, (Jan/Feb 2000), discussing the use of restorative justice principles for "creative options to traditional justice systems, options which are flexible enough to allow positive productive responses to a variety of offenses or violations and which also meet the unique needs of the University community." | |
| Incorporating restorative approaches | 82-page PDF topic guide which presents a, "session plan, guidance and resources for training day focusing on incorporating restorative approaches. Aims to develop an understanding of restorative approaches and their role in behaviour and attendance improvement. The aim is also [to] develop an understanding of the leadership issues in incorporating restorative approaches and explore how restorative approaches might be developed in [one's] own setting." Also available is a related set of 12 slides in ppt format for use in training event. | |
| Media Toolkit for Restorative Justice Organisations | This 100+ page media toolkit presents 10 chapters of practical advice on doing a promotional campaign supporting restorative justice. It was prepared within the framework of the project Building social support for restorative justice, implemented by the European Forum for Restorative Justice (EFRJ) and the partner organisations, between April 2008 and April 2010, and co-financed by the European Commission. The Building social support for restorative justice project has tried to answer three main questions: 1) How can interaction and cooperation with the media be set up in order to inform and educate the public about restorative justice (RJ)? 2) How can cooperation be developed with civil society organi- sations in order to create broad support for RJ? 3) How can we increase the involvement of individual citizens in the functioning of local RJ programmes? The resulting media toolkit covers the following topics: Tool one - Strategic communication planning Tool two - Understanding the media Tool three - Building media relationships Tool four: Developing ethical guideline Tool five - Press release and media events Tool six– Giving interviews Tool seven- Media public campaigns Tool eight- Exploring new media Tool nine- Communication for social change Tool ten- Taking design seriously | |
| Restorative Interventions Implementation Tool Kit | Implementation tools and resources for school staff and other adults trained to facilitate conferences and circles to repair harm in educational settings. The tools and resources are designed to assess readiness, implementation and outcomes, as well provide guidance for implementing any school-based restorative model. | |
| Using encouragement | Document which discusses discouraging verbal messages, encouragement and how to teach problem solving skills adapted from Robert J. Mackenzie's book, "Setting limits in the classroom: How to move beyond the classroom dance of discipline." | |
| The Role of Restorative Justice in Teen Courts: A Preliminary Look | In March 2000, the American Probation and Parole Association convened a focus group to examine and discuss the role of restorative justice in teen court programs (also called youth and peer courts). The panel consisted of persons working actively in teen courts and persons working actively in more traditional restorative justice-based programs. This paper provides a brief overview of restorative justice principles and addresses several key issues the focus group members identified that serve as a promising foundation from which teen courts can begin to move toward integrating more restorative justice-based practices within their programs. Key issues discussed include how youth courts can rethink the role of victims and the community within their programs, how youth courts can alter the way that their proceedings and practices are structured, and how youth courts can rethink and redefine sentencing options so that they are based on the restorative justice philosophy. | |
| Facilitation Guide for Restorative Justice Community Accountability Panel Members | This manual is designed to assist a Trainer in conducting sessions for the purpose of teaching facilitation skills to members of Restorative Justice Community Accountability Panels, or other models of Restorative Justice. It was prepared by using taped transcripts of Training Sessions held for Chilliwack Restorative Justice and Youth Diversion Association, presented by Wendy Burton, professor at the University College of the Fraser Valley. Content has been edited. The information contained in this manual covers the basics of communication and facilitation skills. The manual contains three parts: a participant guide, a trainer's guide, and a collection of handouts and exercises. |
